cp-library
This documentation is automatically generated by online-judge-tools/verification-helper
 argsort
argsort
(cp_library/alg/iter/arg/argsort_fn.py)
- View this file on GitHub
- Last update: 2025-06-20 03:24:59+09:00
Description
argsort returns the indices that would sort an array, using a highly optimized bit-packing approach that’s particularly efficient when run with PyPy.
Usage
from cp_library.alg.iter.arg.argsort_fn import argsort
# Ascending sort indices
indices = argsort(array)
# Descending sort indices
indices = argsort(array, reverse=True)
Implementation Details
The function uses bit-packing to combine array values with their indices before sorting. This approach requires only a single sorting operation, with no costly key functions or multiple passes.
Despite using bit operations, argsort correctly handles negative integers. This works because Python’s left shift operation preserves the relative ordering of numbers, and the bit masking cleanly extracts just the index portion.
PyPy Performance Advantage
The implementation excels when run with PyPy due to:
- Optimized Integer Lists: PyPy uses specialized storage for homogeneous integer arrays
-
Efficient JIT Compilation: Bit operations (
<<,|,&) are highly optimized -
Fast Sorting: PyPy’s
list.sort()is particularly efficient for homogeneous types
Performance Comparison
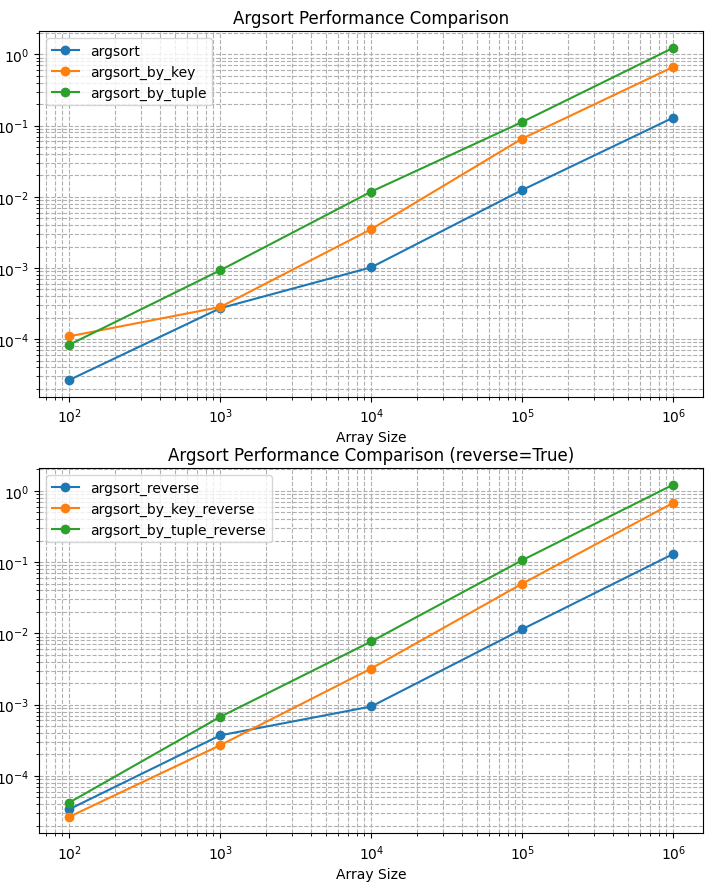
As the benchmark shows, argsort significantly outperforms alternatives:
- ~3-4x faster than
argsort_by_key - ~10x faster than
argsort_by_tuplefor large arrays
For reference, here are the slower but more intuitive alternatives:
def argsort_by_key(A, reverse=False):
I = [*range(len(A))]
I.sort(key=A.__getitem__, reverse=reverse)
return I
def argsort_by_tuple(A, reverse=False):
I = [(a,i) for i,a in enumerate(A)]
I.sort(reverse=reverse)
return [i for _,i in I]
These implementations perform poorly compared to argsort primarily due to:
- Function call overhead with the key-based approach
- Memory allocation overhead for creating tuples
- Less effective JIT optimization by PyPy
Depends on
Required by
 cp_library/alg/graph/fast/digraph_weighted_cls.py
cp_library/alg/graph/fast/digraph_weighted_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/graph/fast/digraph_weighted_meta_cls.py
cp_library/alg/graph/fast/digraph_weighted_meta_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/graph/fast/graph_weighted_base_cls.py
cp_library/alg/graph/fast/graph_weighted_base_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/graph/fast/graph_weighted_cls.py
cp_library/alg/graph/fast/graph_weighted_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/graph/fast/graph_weighted_meta_cls.py
cp_library/alg/graph/fast/graph_weighted_meta_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/iter/arg/argsort_bounded_fn.py
cp_library/alg/iter/arg/argsort_bounded_fn.py
 cp_library/alg/iter/sort/isort_parallel_fn.py
cp_library/alg/iter/sort/isort_parallel_fn.py
 cp_library/alg/iter/sort/sort_parallel_fn.py
cp_library/alg/iter/sort/sort_parallel_fn.py
 cp_library/alg/tree/fast/aux_tree_base_cls.py
cp_library/alg/tree/fast/aux_tree_base_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/tree/fast/aux_tree_cls.py
cp_library/alg/tree/fast/aux_tree_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/tree/fast/aux_tree_weighted_cls.py
cp_library/alg/tree/fast/aux_tree_weighted_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/tree/fast/hld_weighted_cls.py
cp_library/alg/tree/fast/hld_weighted_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/tree/fast/tree_weighted_base_cls.py
cp_library/alg/tree/fast/tree_weighted_base_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/tree/fast/tree_weighted_cls.py
cp_library/alg/tree/fast/tree_weighted_cls.py
 cp_library/alg/tree/fast/tree_weighted_meta_cls.py
cp_library/alg/tree/fast/tree_weighted_meta_cls.py
Verified with
 test/aoj/grl/grl_1_a_fast_dijkstra.test.py
test/aoj/grl/grl_1_a_fast_dijkstra.test.py
 test/aoj/grl/grl_1_b_fast_bellman_ford.test.py
test/aoj/grl/grl_1_b_fast_bellman_ford.test.py
 test/aoj/grl/grl_1_c_fast_floyd_warshall.test.py
test/aoj/grl/grl_1_c_fast_floyd_warshall.test.py
 test/aoj/grl/grl_5_a_fast_diameter.test.py
test/aoj/grl/grl_5_a_fast_diameter.test.py
 test/aoj/grl/grl_5_b_fast_height.test.py
test/aoj/grl/grl_5_b_fast_height.test.py
 test/aoj/vol/0439_aux_dijkstra.test.py
test/aoj/vol/0439_aux_dijkstra.test.py
 test/aoj/vol/0439_aux_rerooting_dp.test.py
test/aoj/vol/0439_aux_rerooting_dp.test.py
 test/aoj/vol/0439_aux_weighted_rerooting_dp.test.py
test/aoj/vol/0439_aux_weighted_rerooting_dp.test.py
 test/atcoder/abc/abc294_g_fast_tree_hld.test.py
test/atcoder/abc/abc294_g_fast_tree_hld.test.py
 test/atcoder/abc/abc294_g_fast_tree_hld_bit.test.py
test/atcoder/abc/abc294_g_fast_tree_hld_bit.test.py
 test/atcoder/abc/abc294_g_fast_tree_lca_table_weighted_bit.test.py
test/atcoder/abc/abc294_g_fast_tree_lca_table_weighted_bit.test.py
 test/library-checker/graph/incremental_scc.test.py
test/library-checker/graph/incremental_scc.test.py
 test/library-checker/graph/incremental_scc_paralel_sort.test.py
test/library-checker/graph/incremental_scc_paralel_sort.test.py
 test/library-checker/graph/minimum_spanning_tree_kruskal.test.py
test/library-checker/graph/minimum_spanning_tree_kruskal.test.py
 test/library-checker/graph/minimum_spanning_tree_kruskal_heap.test.py
test/library-checker/graph/minimum_spanning_tree_kruskal_heap.test.py
 test/library-checker/graph/shortest_path_fast_graph.test.py
test/library-checker/graph/shortest_path_fast_graph.test.py
 test/library-checker/graph/shortest_path_min_heap.test.py
test/library-checker/graph/shortest_path_min_heap.test.py
 test/library-checker/tree/tree_diameter.test.py
test/library-checker/tree/tree_diameter.test.py
 test/library-checker/tree/tree_path_composite_sum.test.py
test/library-checker/tree/tree_path_composite_sum.test.py
 test/yukicoder/3407.test.py
test/yukicoder/3407.test.py
Code
import cp_library.__header__
import cp_library.alg.__header__
import cp_library.alg.iter.__header__
import cp_library.alg.iter.arg.__header__
def argsort(A: list[int], reverse=False):
s, m = pack_sm(len(A))
if reverse:
I = [a<<s|m^i for i,a in enumerate(A)]
I.sort(reverse=True)
for i,ai in enumerate(I): I[i] = m^ai&m
else:
I = [a<<s|i for i,a in enumerate(A)]
I.sort()
for i,ai in enumerate(I): I[i] = ai&m
return I
from cp_library.bit.pack.pack_sm_fn import pack_sm'''
╺━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╸
https://kobejean.github.io/cp-library
'''
def argsort(A: list[int], reverse=False):
s, m = pack_sm(len(A))
if reverse:
I = [a<<s|m^i for i,a in enumerate(A)]
I.sort(reverse=True)
for i,ai in enumerate(I): I[i] = m^ai&m
else:
I = [a<<s|i for i,a in enumerate(A)]
I.sort()
for i,ai in enumerate(I): I[i] = ai&m
return I
def pack_sm(N: int): s=N.bit_length(); return s,(1<<s)-1